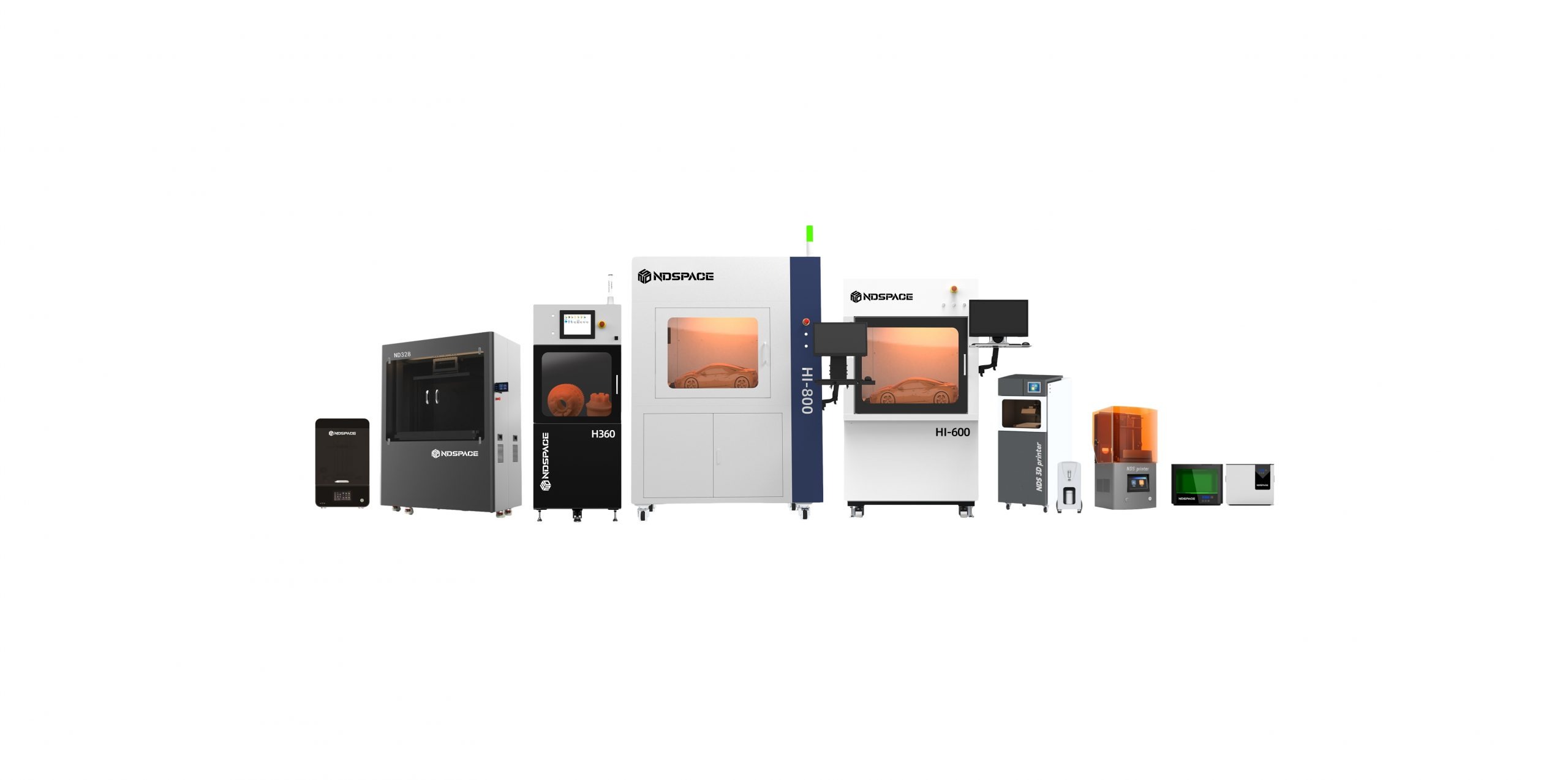
In the rapidly evolving landscape of manufacturing, industrial 3D printing has emerged as a transformative force, revolutionizing traditional production processes. This blog explores the development of industrial 3D printing and its significant impact on various industries, shedding light on its applications, advantages, and future prospects.
Introduction to Industrial 3D Printing
Industrial 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, involves the creation of three-dimensional objects through the layer-by-layer deposition of materials based on digital models. This innovative technology has a rich history, evolving from its inception as a rapid prototyping tool to a game-changing manufacturing method. Industrial 3D printing technologies encompass diverse processes such as laser sintering and electron beam melting, offering unparalleled design freedom and production capabilities.
Applications and Benefits of Industrial 3D Printing
The applications of industrial 3D printing span across a multitude of industries including automotive, aerospace, and healthcare. This technology empowers engineers and designers with enhanced flexibility, enabling the creation of complex geometries and customized components. Moreover, industrial 3D printing drives cost-effectiveness by minimizing material waste and optimizing production speed, leading to streamlined manufacturing workflows.
Comparison with Traditional Manufacturing Methods
In comparison to traditional manufacturing processes, industrial 3D printing presents distinct advantages. The conventional methods, characterized by subtractive manufacturing, are being challenged by the superior capabilities of additive manufacturing. Real-world examples showcase the prowess of 3D printing in delivering intricate, lightweight components with reduced lead times, marking a paradigm shift in the manufacturing landscape.
Future Prospects and Advancements in Industrial 3D Printing
The future of industrial 3D printing is poised for remarkable advancements, with ongoing innovations in materials and technologies. Additive manufacturing is set to exert a significant impact on supply chains and production workflows, driving efficiency and agility. The integration of advanced materials further expands the horizons of industrial 3D printing, promising novel applications and breakthroughs in manufacturing.
Conclusion
The rise of industrial 3D printing signifies a monumental shift in the manufacturing domain, offering industry professionals, engineers, and manufacturers a glimpse into the future of production. As this technology continues to advance, it is imperative for stakeholders to recognize its transformative potential and adapt to the evolving landscape of manufacturing. Industrial 3D printing stands as a beacon of innovation, shaping the future of production with its rapid, efficient, and technologically-driven approach.
In summary, the development of industrial 3D printing reflects a revolution in manufacturing processes, fueling a demand for advanced, efficient solutions that are reshaping the industry’s landscape. With its potential to drive rapid, cost-effective production and enable unparalleled design flexibility, industrial 3D printing stands as a testament to the transformative power of cutting-edge technologies.